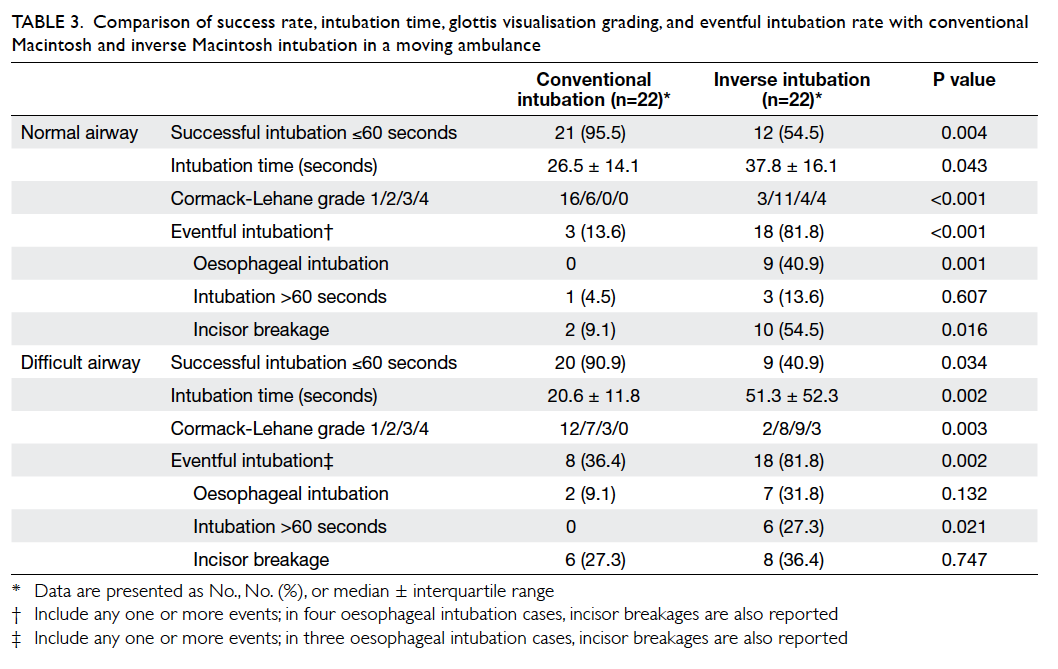
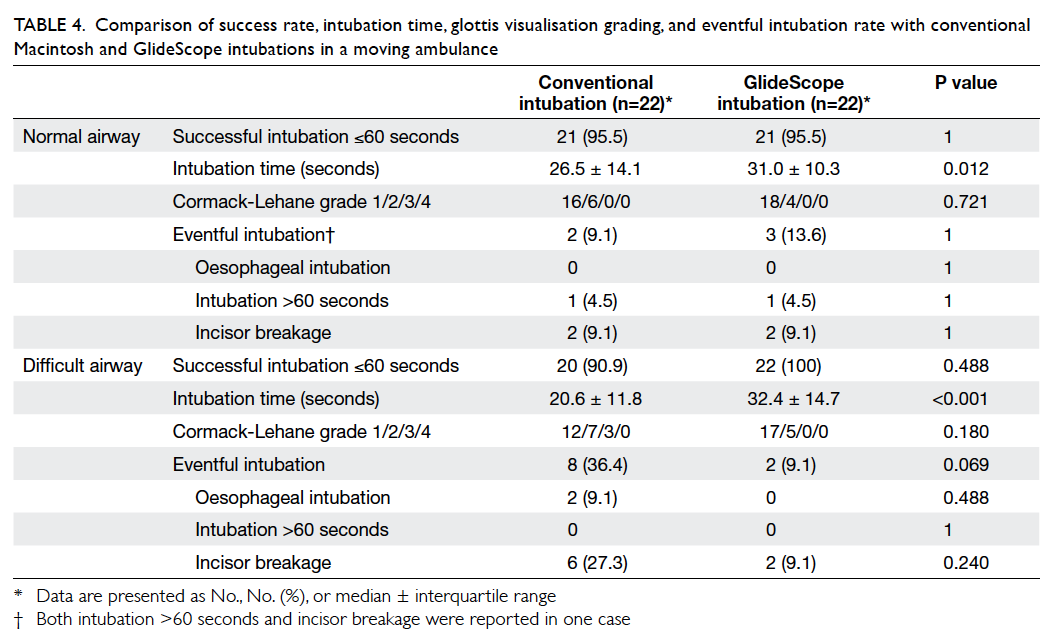
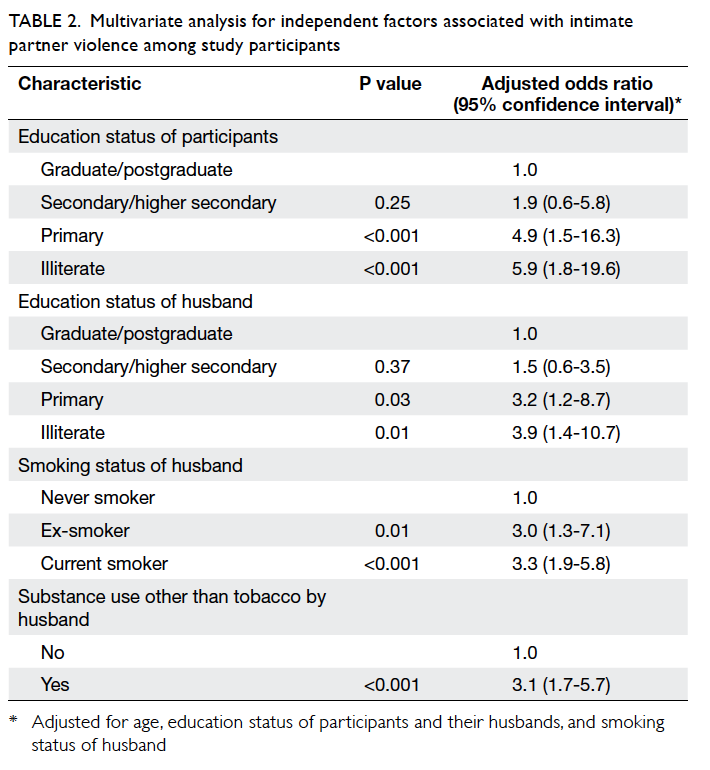
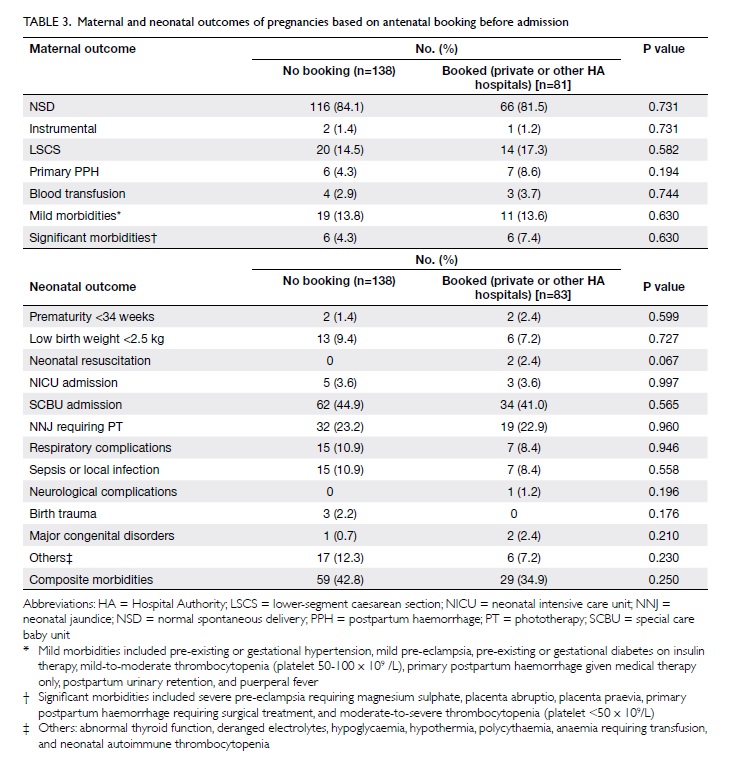
Limitation of radiological T3 subclassification of rectal cancer due to paucity of mesorectal fat in Chinese patients
Hong
Kong Med J 2014 Oct;20(5):366–70 | Epub 1
Aug 2014
DOI: 10.12809/hkmj144232
© Hong Kong Academy of Medicine. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Limitation of radiological T3 subclassification
of
rectal cancer due to paucity of mesorectal fat in
Chinese patients
Esther MF Wong, FHKCR, FHKAM (Radiology)1;
Bill MH Lai, MB, BS, FRCR1; Vincent KP Fung, MB, BS,
FRCR1; Hester YS Cheung, FRACS, FHKAM (Surgery)2;
WT Ng, FHKCR, FHKAM (Radiology)3; Ada LY Law, FHKCR,
FHKAM (Radiology)3; Alta YT Lai, MB, BS1;
Jennifer LS Khoo, FHKCR, FHKAM (Radiology)1
1Department of Radiology,
Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Chai Wan, Hong Kong
2Department of Surgery,
Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Chai Wan, Hong Kong
3Department of Oncology,
Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Chai Wan, Hong Kong
Corresponding author: Dr Esther MF Wong (esthermfwong@gmail.com)
Abstract
Objectives: To describe
the thickness of mesorectal
fat in local Chinese population and its impact on
rectal cancer staging.
Design: Case series.
Setting: Two local
regional hospitals in Hong Kong.
Patients: Consecutive
patients referred for
multidisciplinary board meetings from January to
October 2012 were selected.
Main outcome measures:
Reports of cases
that had undergone staging magnetic resonance
imaging for histologically proven rectal cancer
were retrospectively retrieved and reviewed by
two radiologists. All magnetic resonance imaging
examinations were acquired with 1.5T magnetic
resonance imaging. Measurements were made
by agreement between the two radiologists. The
distance in mm was obtained in the axial plane at
levels of 5 cm, 7.5 cm, and 10 cm from the anal verge.
Four readings were obtained at each level, namely,
anterior, left lateral, posterior, and right lateral
positions.
Results: A total of 25
patients (16 males, 9 females)
with a median age of 69 (range, 38-84) years were
included in the study. Mean thickness of the
mesorectal fat at 5 cm, 7.5 cm, and 10 cm from
the anal verge was 3.1 mm (standard deviation, 3.0
mm), 9.8 mm (5.3 mm), and 11.8 mm (4.2 mm),
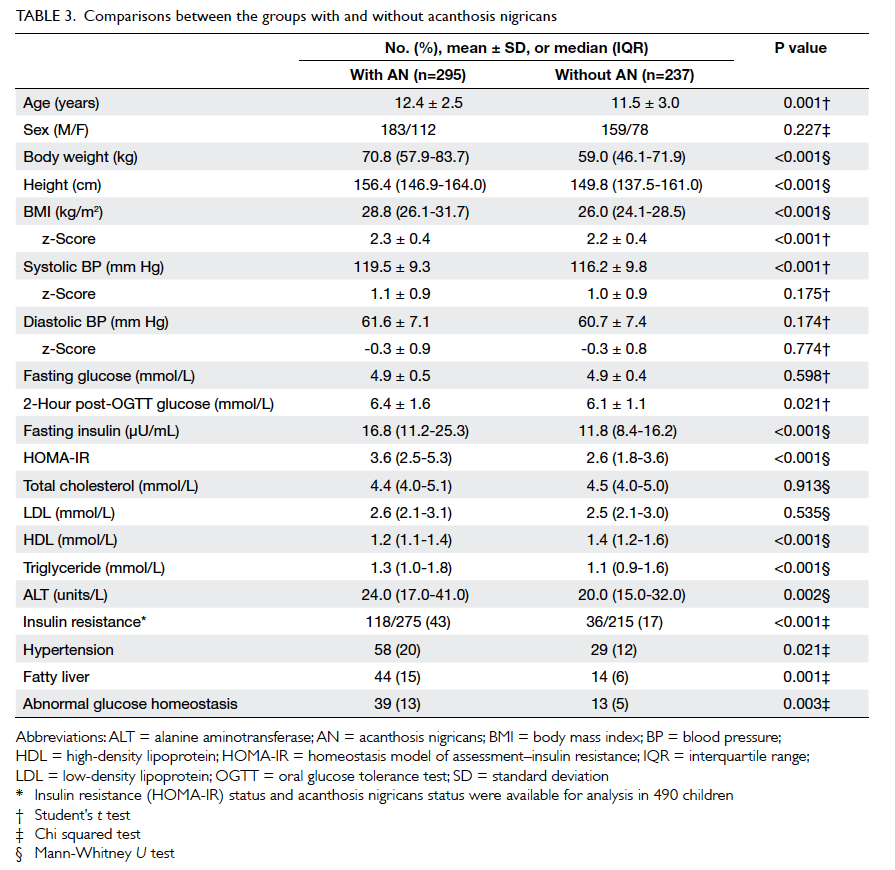
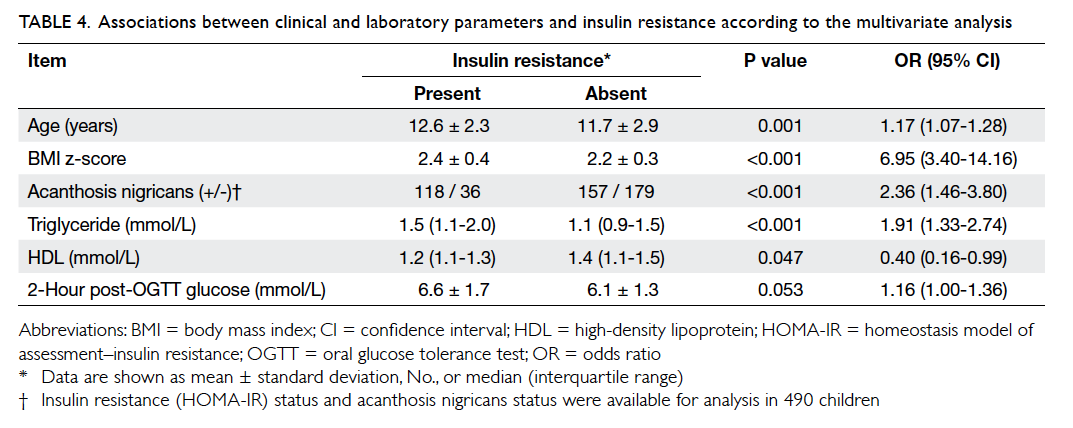
respectively. The proportions of patients with mean mesorectal
fat thickness of <15 mm were
100%, 84%, and 75% at 5 cm, 7.5 cm, and 10 cm
from the anal verge, respectively. The thickness of
mesorectal fat was the least anteriorly, and <15 mm at all
three arbitrary levels (P<0.001).
Conclusion: The
thickness of mesorectal fat was
<15 mm in the majority of patients and
in most positions. Tumours invading 10 mm
beyond the serosa on magnetic resonance imaging
may paradoxically threaten the circumferential
resection margin in Chinese patients. Use of T3
subclassification of rectal cancer in Chinese patients
may be limited.
New knowledge added by this
study
- Paucity of mesorectal fat in Chinese populations: tumours invading 10 mm beyond the serosa on magnetic resonance imaging may threaten the circumferential resection margin in the majority of patients.
- The mesorectal fat is thinnest in the anterior portion. Tumours in the anterior wall have a higher chance of infiltrating the mesorectal fascia versus those located in other positions.
- The T3 subclassification of rectal cancer should be used with caution in Chinese patients.
Introduction
Rectal cancer is associated with a high
risk of distant
metastases as well as local recurrence. The reported
local recurrence rate after surgical treatment was
up to 32% in some older literatures.1
Recently,
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as a powerful local
staging tool which also helps to
guide subsequent management plan.2
3 The status of
circumferential resection margin (CRM), presence of
lymph node metastasis, and location of the tumour,
all of which can be predicted on MRI, are important
prognostic factors for pelvic disease recurrence after treatment
with curative intent (local failure).4
5 6
The depth of extramural penetration of the
tumour has been shown to be an independent
prognostic factor.7
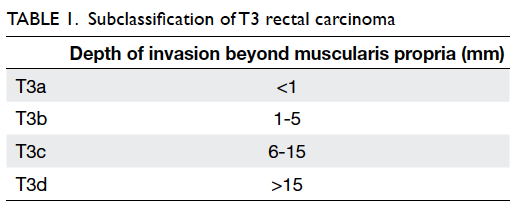
According to the European
Society for Medical Oncology guidelines,8
T3 disease
is subclassified into T3a, T3b, T3c, and T3d based
on the depth of invasion beyond the muscularis
propria (Table
1). Magnetic resonance imaging is
also highly accurate in predicting the actual depth of
this invasion.9 Currently,
patients with disease more
advanced than T3b are recommended to receive
induction therapy prior to surgery.
Another factor that potentially affects the
disease status is the thickness of the mesorectal
fat which, for the sake of this discussion, shall be
defined as the distance between the serosa and
mesorectal fascia. The word ‘perirectal fat’ is used
interchangeably with ‘mesorectal fat’. We are of
the opinion that the word ‘mesorectal fat’ better
conceptualises compartmentalised fat within the
mesorectal fascia and is, thus, selected for use in this
article.
In our experience, the mesorectal fat is
rather
thin in Chinese patients. It is not uncommon to
encounter early T3 (T3a/b) disease with threatened
CRM as predicted on MRI. The less the mesorectal
fat thickness, the less the depth of extramural
invasion it takes to infiltrate the CRM.
This study aimed to measure the amount of
mesorectal fat in the local population. The use and
limitation of T3 subclassification in the Chinese
population will be discussed.
Methods
A total of 25 consecutive staging MRIs done
for patients referred for rectal carcinoma
multidisciplinary meetings at a local regional hospital from
January to October 2012
were retrospectively reviewed by two radiologists
with special interest in abdominal imaging.
All MRI examinations were acquired with
1.5T MRIs in two local centres using Siemens
Magnetom Avanto (Erlangen, Germany) MRI
machines. Measurements were made with mutual
agreement between the two reviewing radiologists.
The thickness of mesorectal fat was defined as the
distance from the serosa to the mesorectal fascia in
the axial plane. The distance in mm was obtained
in the true axial plane at levels of 5 cm, 7.5 cm, and
10 cm from the anal verge. Measurements were
performed primarily on T2 sequence, supplemented
by T1 sequence if the acquired T2 images were
unsatisfactory. As this study involved two hospitals,
the scanning parameter was not identical. However,
such difference was not assumed to attribute to error of any
source in terms of calibre measurement.
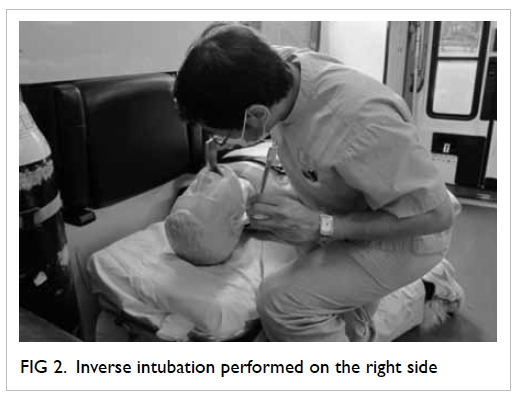
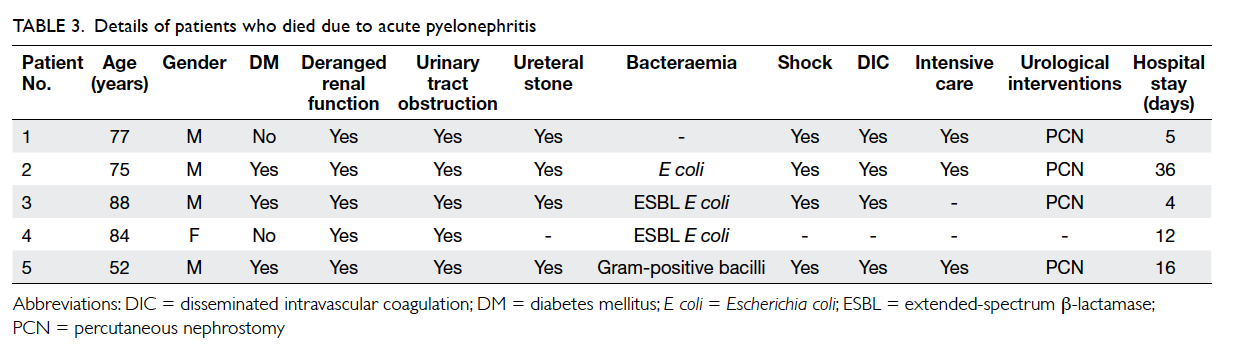
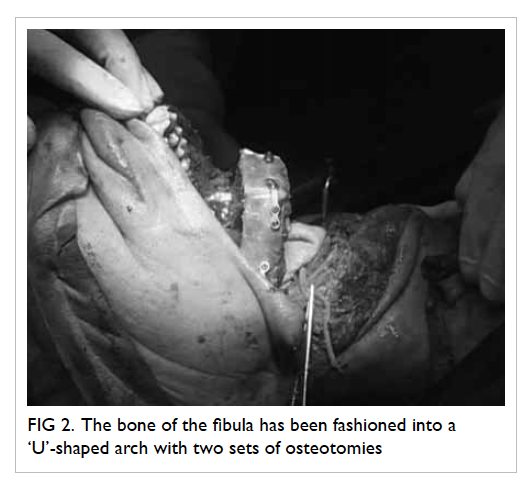
Four readings were obtained at each level,
namely, anterior, left lateral, posterior, and right
lateral positions (Fig
1).
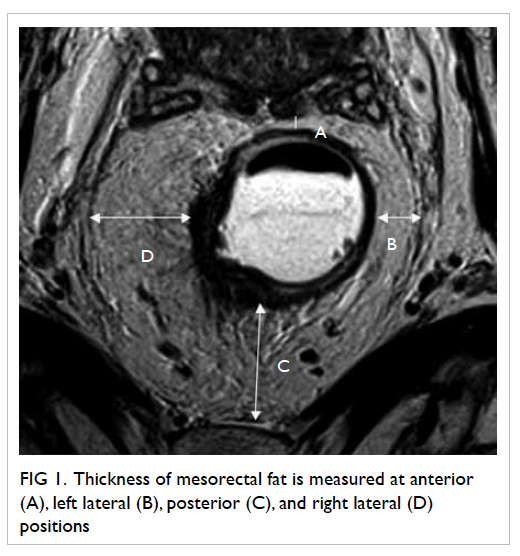
Figure 1. Thickness of mesorectal fat is measured at anterior (A), left lateral (B), posterior (C) and right lateral (D) positions
Patients with bulky primary or secondary
pelvic
tumours (>3 cm in diameter) were excluded from
the study, as these might potentially cause significant
distortion of the anatomy and configuration of the
mesorectum.
Statistical analysis was performed with the
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (Windows
version 15.0; SPSS Inc, Chicago [IL], US). One-sample
Student’s t test was performed for analysis of
mean thickness.
Results
A total of 25 patients (16 males, 9
females) with a median age of 69 (range, 38-84) years were
included
in the study. The rectosigmoid junctions were
reached at the level of 10 cm above the anal verge
for four patients and were, thus, excluded from
calculation for the respective level.
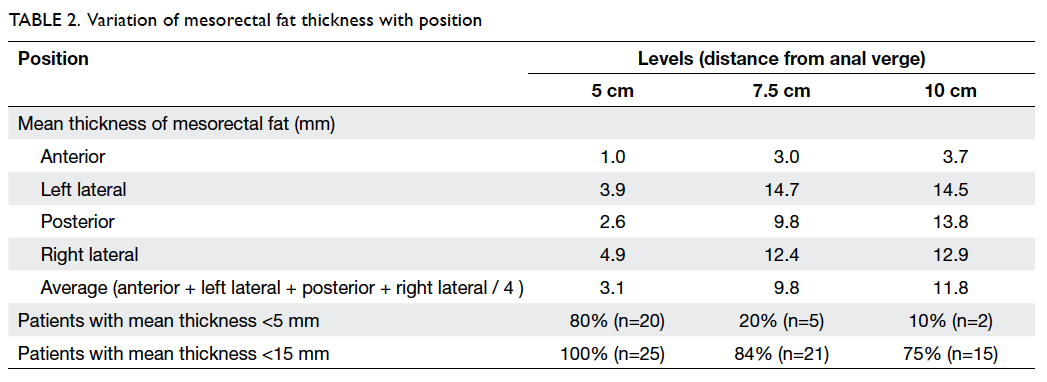
Mean thicknesses of mesorectal fat at 5 cm,
7.5 cm,
and 10 cm from the anal verge were 3.1 (standard
deviation [SD]=3.0) mm, 9.8 (SD=5.3) mm, and
11.8 (SD=4.2) mm, respectively. Details of the
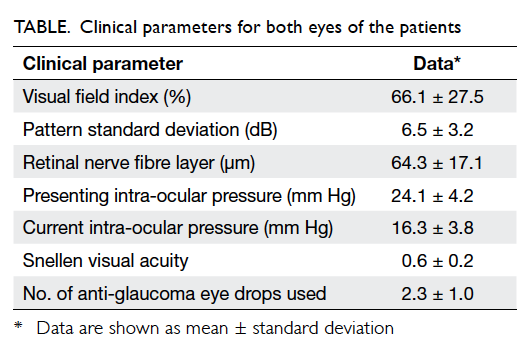
mean mesorectal fat thickness are shown in Table
2. In brief, the proportions of patients with mean
mesorectal fat thickness of <15 mm were
100%, 84%, and 75% at 5 cm, 7.5 cm, and 10 cm from
the anal verge, respectively.
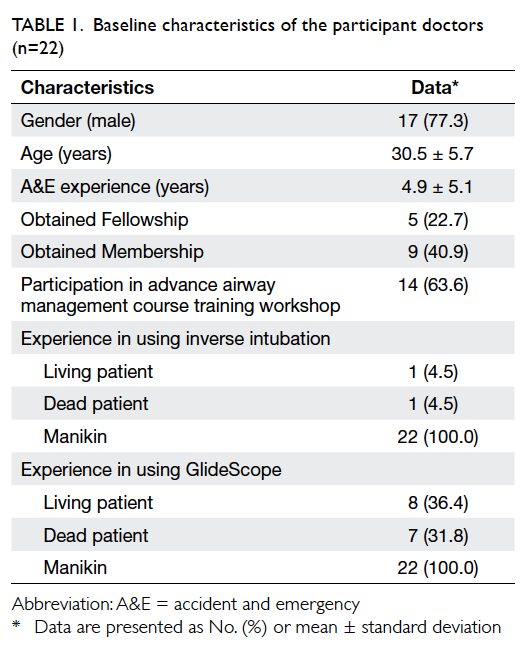
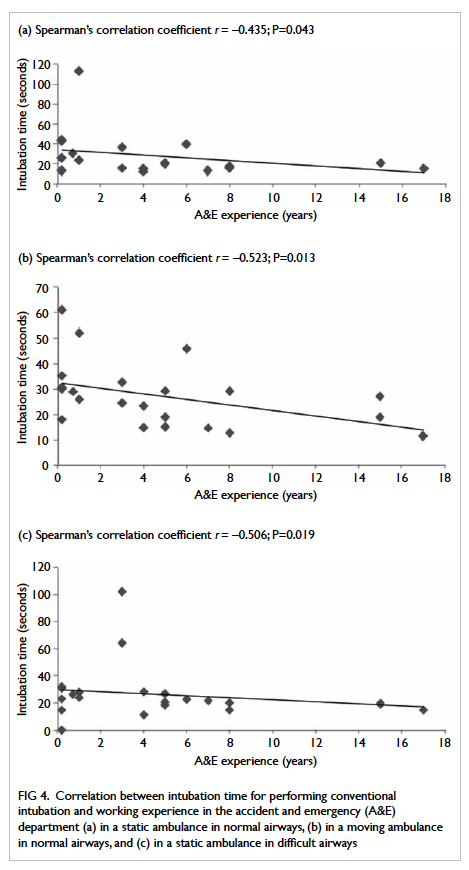
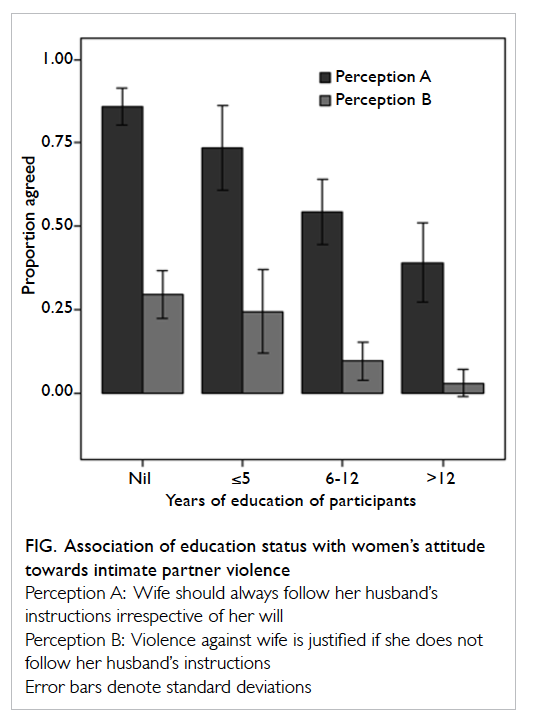
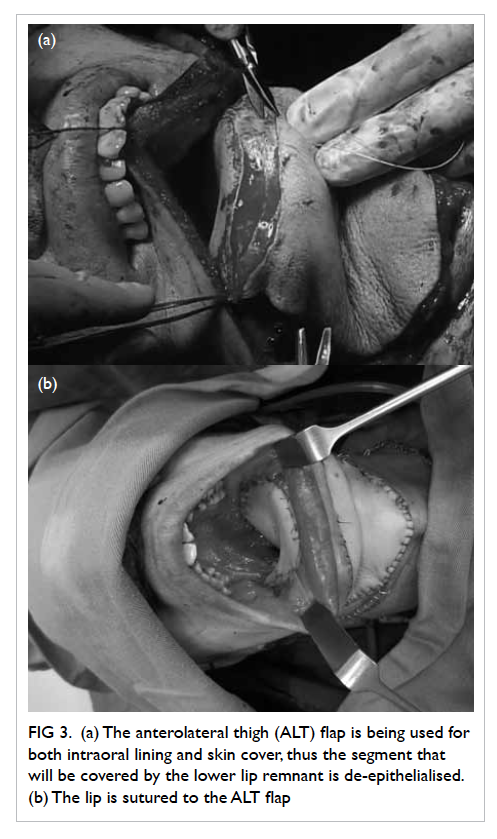
The mesorectal fat was noted to be the
least
thick in the anterior position for all three arbitrary
levels (Table
2; Fig
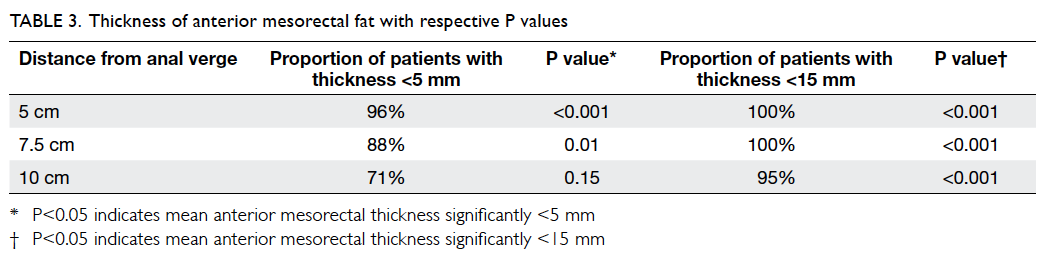
2). At 5 cm and 7.5 cm from the anal verge, proportions of
patients with mesorectal
fat thickness of <5 mm were 96% and 88%,
respectively. The figure reached up to 100% if 15 mm
was taken as the cutoff level. At 10 cm from the
anal verge, 95% of patients showed mesorectal fat
thickness of <15 mm. t Tests showed that the
anterior mesorectal fat thickness was significantly
<15 mm at all three levels (P<0.001) and
<5 mm at both 5 cm (P<0.001) and 7.5 cm
(P=0.01) from the anal verge (Table
3).
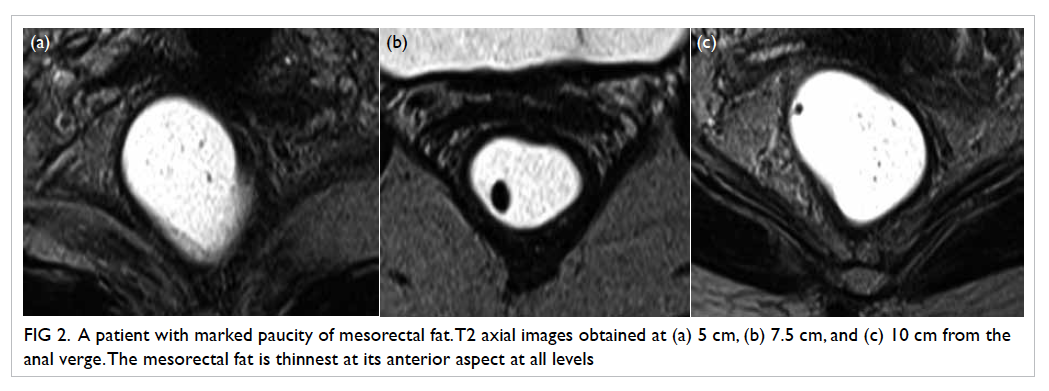
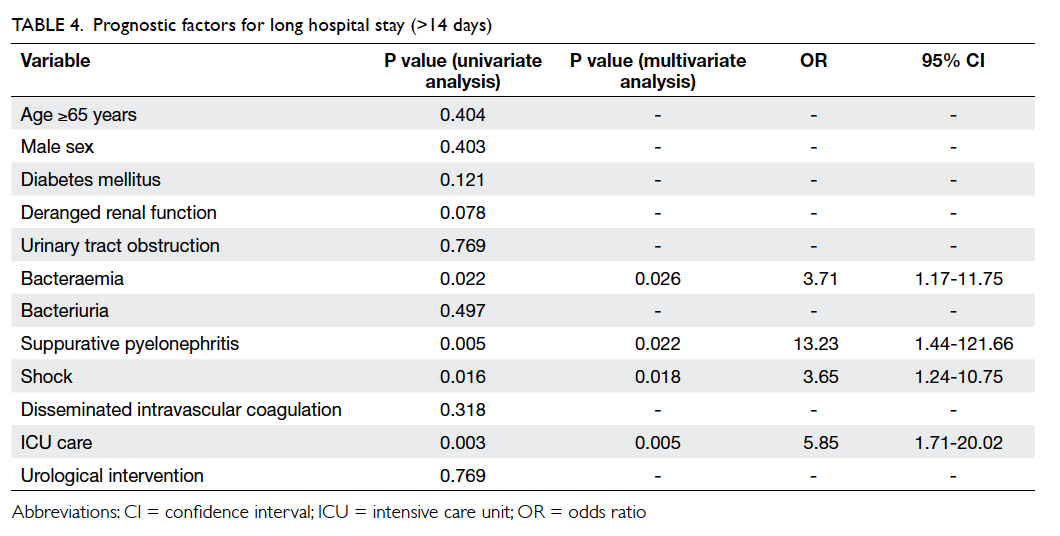
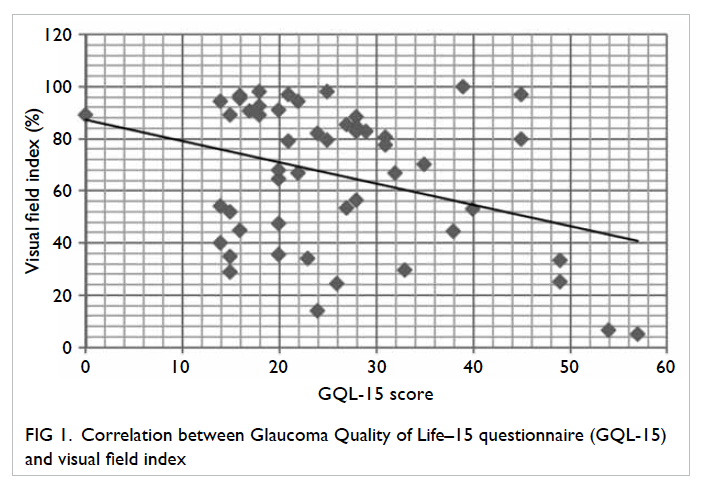
Figure 2. A patient with marked paucity of mesorectal fat. T2 axial images obtained at (a) 5 cm, (b) 7.5 cm, and (c) 10 cm from the anal verge. The mesorectal fat is thinnest at its anterior aspect at all levels
There was a tendency for the lateral
aspects
to be more spacious than the anterior and posterior
aspects, and for the left side to be larger than the right
side. However, these findings were not statistically
significant.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the
first
Chinese study and the first study in Asian subjects
on mesorectal fat thickness. The majority of
published literature on MRI staging of carcinoma
of rectum are based, predominantly, on data from
western/Caucasian populations. It has been well
known that variations in body build, lean mass, and
fat composition do occur across ethnic groups.10
Chinese or Asian patients have a smaller body build.
Whether the amount of fat in the mesorectum is the
same in Chinese and Caucasian population remains
largely unknown.
In recent decades, total mesorectal
excision
has revolutionised rectal cancer surgery.11
Patients
with relatively early tumours (ie T3b or below,
lymph node–negative) are usually streamlined to
total mesorectal excision without preoperative
neoadjuvant therapy. The rationale behind this is
that early, mid- and low-rectal tumours with their
whole lymphatic drainage are contained within the
mesorectal fascia. Total mesorectal excision allows
en-bloc removal of the tumour together with its
intact mesorectal fascia. A low local recurrence rate
of only 4% has been reported.12
An involved CRM is an independent disease
prognostic indicator.13 It
is defined pathologically as
identifying tumour cells within 1 mm of the surgically
created margin. Beets-Tan et al14
postulated that, on
MRI, a distance of 6 mm from the outer edge of the
tumour to the mesorectal fascia predicted a tumour
distance of 2 mm on histology with 97% confidence,
and a distance of 5 mm could predict a crucial
distance of 1 mm on histology with high confidence.
A study using 1 mm as cutoff showed data with
satisfactory accuracy despite a lower sensitivity.15
For practical purposes, we have adopted a cutoff of
5 mm as the predictor of clear CRM.
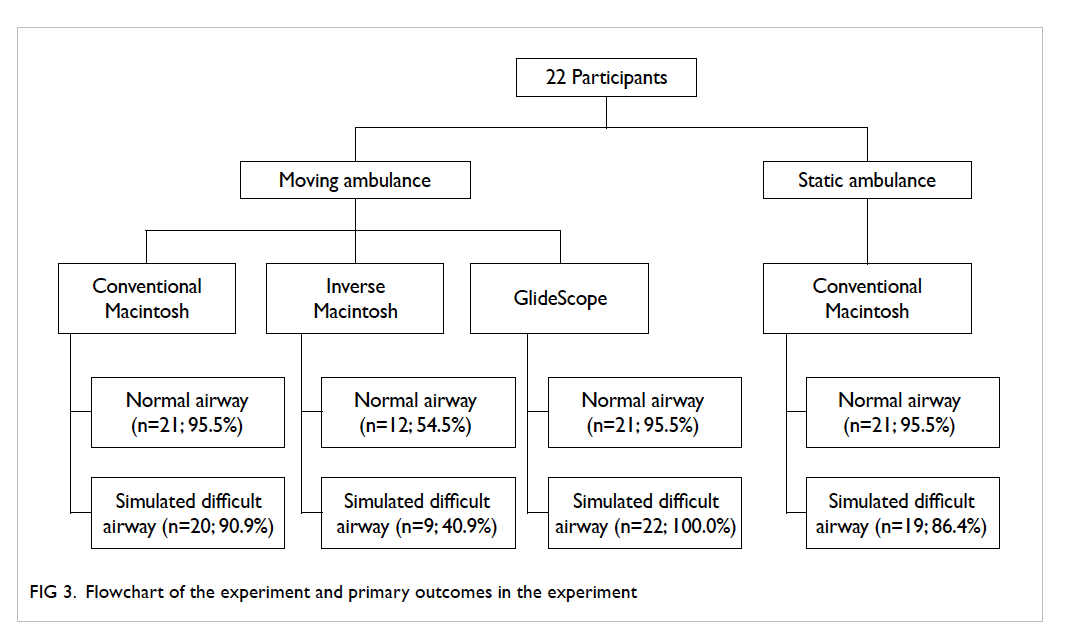
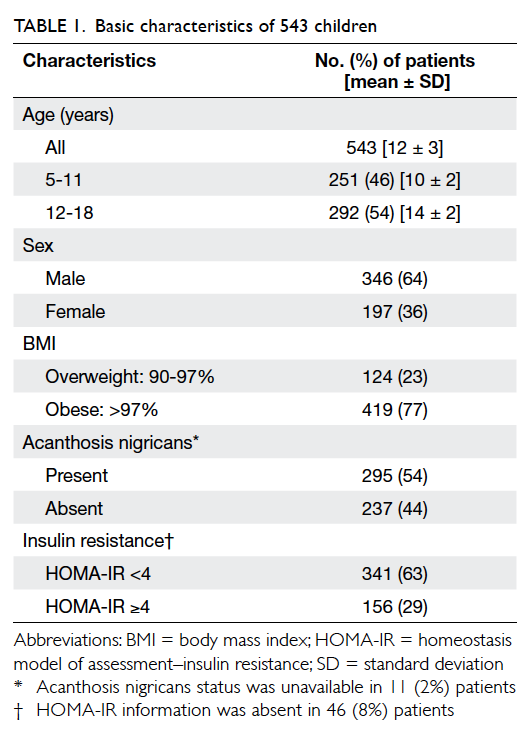
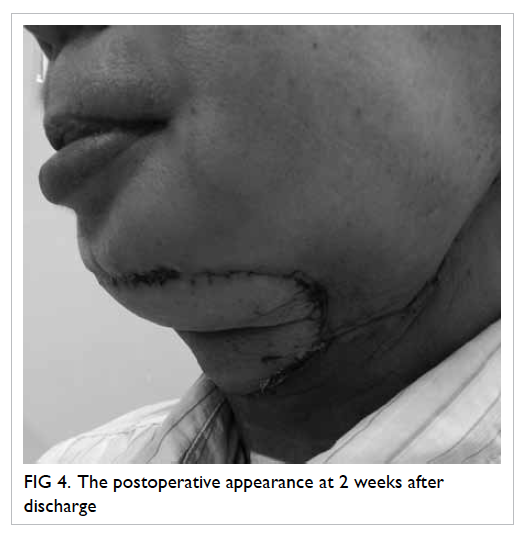
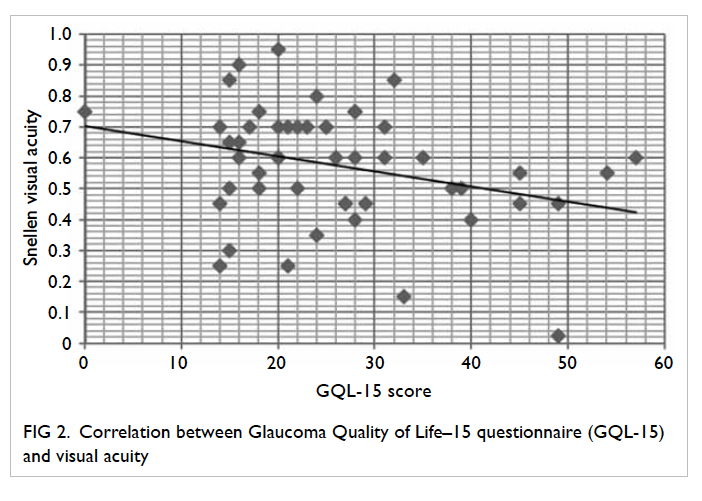
Given a certain depth of tumour invasion,
CRM is more likely to be threatened for patients with
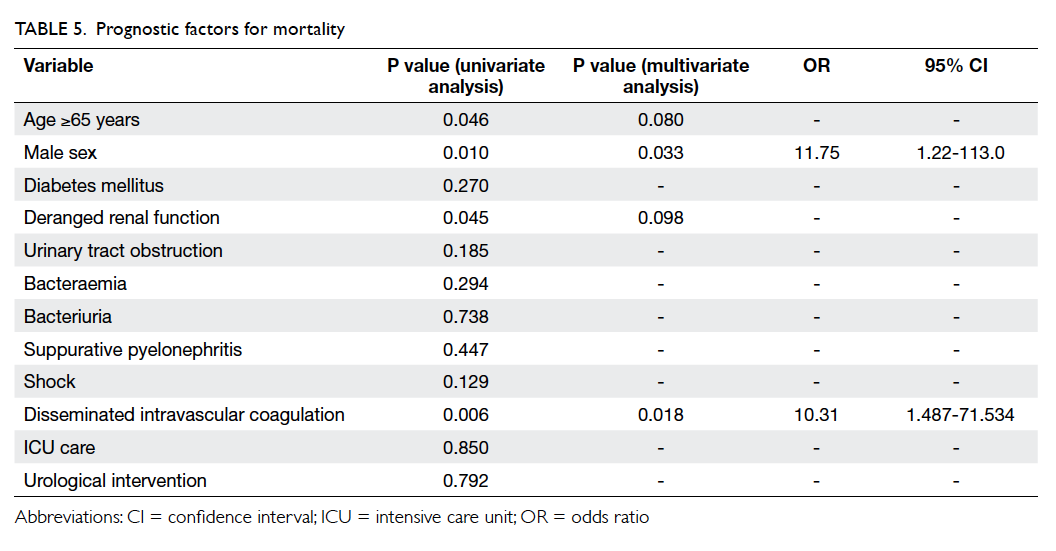
thinner mesorectal fat (Fig
3). The mean thickness of
mesorectal fat is <15 mm for the majority of patients at all
arbitrarily measured levels. Taking
into account the margin of 5 mm on MRI, a tumour
invading 10 mm beyond the serosa on MRI fulfils
the criteria for threatened CRM in the majority of
patients. Whether Chinese patients present with
later-stage disease or have worse disease prognosis is
largely unknown. However, caution has to be taken
that T3a/b disease in Chinese populations does not
equal, or even imply, early-stage disease.
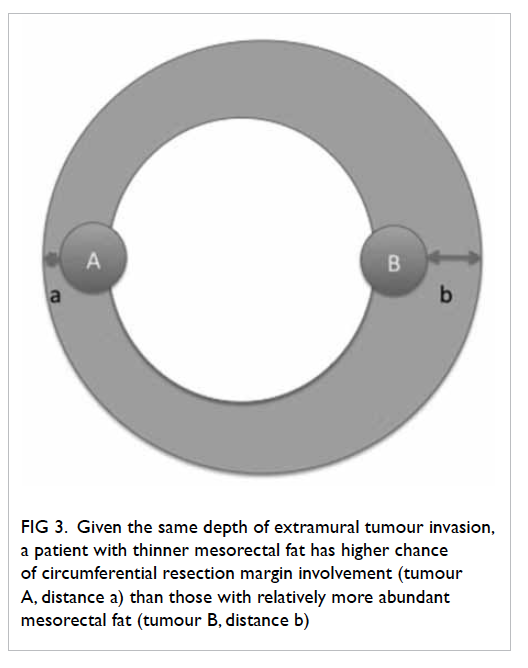
Figure 3. Given the same depth of extramural tumour invasion, a patient with thinner mesorectal fat has higher chance of circumferential resection margin involvement (tumour A, distance a) than those with relatively more abundant mesorectal fat (tumour B, distance b)
The position of the tumour may also affect
the
chance of mesorectal fat infiltration. The anterior
aspect of the mesorectal fat was found to be thinnest
at all three arbitrary levels. This is in agreement with
studies in European populations.16
The postulated
reason is that the anterior mesorectal fat tends to
be compressed by anterior pelvic organs such as the
uterus and prostate when one lies in supine position,
the position where MRI is conventionally acquired.
As a result, anterior tumour tends to threaten the
CRM with relatively shallow subserosal penetration.
The mesorectal fat is thinner inferiorly as
it
approaches the anal verge. Low rectal cancer (<5 cm
from the anal verge) has overall worse prognosis.
Higher local recurrence rate with higher chances
of CRM involvement has been reported.17
This may
be partly explained by the fact that the amount of
mesorectal fat is thinner in low rectum. Low rectal
tumours also deserve special surgical attention.18
One major weakness of this study was that
body mass index (BMI) was not taken into account.
However, a study in the UK19
has shown that BMI does not affect the thickness or volume of
mesorectal
fat. However, the measurement method employed
in that study was different from that in our study,
rendering direct comparison difficult. Whether
the paucity of mesorectal fat in Chinese patients is
due to body build or genetic factors is unknown.
Further multicentre studies with collection of BMI
data and ethnic information and using standardised
measurement methods are needed for better
comparison.
Conclusion
Thickness of mesorectal fat is shown to be
<15 mm in the majority of patients in most positions
and at most levels. It was <5 mm for low rectal
position. T3a/b tumours may paradoxically infiltrate
the mesorectal fascia in the study population. In
staging of Chinese rectal cancer patients, T3a/b
tumours may threaten the CRM in the majority of
locations and patients. Thus, the status of T3a/b
alone should not be taken as an indicator of early-stage
disease.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr John KW
Chan
and St Paul’s Hospital for courtesy of MRI images.
References
1. Sagar PM, Pemberton JH. Surgical
management of locally
recurrent rectal cancer. Br J Surg 1996;83:293-304. CrossRef
2. Beets-Tan RG, Beets GL. Rectal
cancer: review with
emphasis on MR imaging. Radiology 2004;232:335-46. CrossRef
3. Bipat S, Glas AS, Slors FJ,
Zwinderman AH, Bossuyt PM,
Stoker J. Rectal cancer: local staging and assessment of
lymph node involvement with endoluminal US, CT, and
MR imaging—meta-analysis. Radiology 2004;232:773-83. CrossRef
4. Pedersen BG, Moran B, Brown G,
Blomqvist L, Fenger-Grøn M, Laurberg S. Reproducibility of depth
of
extramural tumor spread and distance to circumferential
resection margin at rectal MRI: enhancement of clinical
guidelines for neoadjuvant therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol
2011;197:1360-6. CrossRef
5. van Gijn W, Marijnen CA,
Nagtegaal ID, et al. Preoperative
radiotherapy combined with total mesorectal excision
for resectable rectal cancer: 12-year follow-up of the
multicentre, randomised controlled TME trial. Lancet
Oncol 2011;12:575-82. CrossRef
6. Lahaye MJ, Engelen SM, Nelemans
PJ, et al. Imaging for predicting the risk factors—the
circumferential resection
margin and nodal disease—of local recurrence in rectal
cancer: a meta-analysis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR
2005;26:259-68. CrossRef
7. Shin R, Jeong SY, Yoo HY, et al.
Depth of mesorectal
extension has prognostic significance in patients with T3
rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 2012;55:1220-8. CrossRef
8. Glimelius B, Tiret E, Cervantes
A, Arnold D; ESMO
Guidelines Working Group. Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical
Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up.
Ann Oncol 2013;24 Suppl 6:vi81-8. CrossRef
9. MERCURY Study Group. Extramural
depth of tumor
invasion at thin-section MR in patients with rectal cancer:
results of the MERCURY study. Radiology 2007;243:132-9. CrossRef
10. Lear SA, Kohli S, Bondy GP,
Tchernof A, Sniderman
AD. Ethnic variation in fat and lean body mass and the
association with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab 2009;94:4696-702. CrossRef
11. Heald RJ, Ryall RD. Recurrence
and survival after
total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Lancet
1986;327:1479-82. CrossRef
12. Heald RJ, Moran BJ, Ryall RD,
Sexton R, MacFarlane
JK. Rectal cancer: the Basingstoke experience of total
mesorectal excision, 1978-1997. Arch Surg 1998;133:894-9. CrossRef
13. Bernstein TE, Endreseth BH,
Romundstad P, Wibe A;
Norwegian Colorectal Cancer Group. Circumferential
resection margin as a prognostic factor in rectal cancer. Br
J Surg 2009;96:1348-57. CrossRef
14. Beets-Tan RG, Beets GL,
Vliegen RF, et al. Accuracy of
magnetic resonance imaging in prediction of tumour-free
resection margin in rectal cancer surgery. Lancet
2001;357:497-504. CrossRef
15. MERCURY Study Group.
Diagnostic accuracy of
preoperative magnetic resonance imaging in predicting
curative resection of rectal cancer: prospective
observational study. BMJ 2006;333:779. CrossRef
16. Torkzad MR, Blomqvist L. The
mesorectum: morphometric
assessment with magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol
2005;15:1184-91. CrossRef
17. Nagtegaal ID, van de Velde CJ,
Marijnen CA, van Krieken
JH, Quirke P; Dutch Colorectal Cancer Group; Pathology
Review Committee. Low rectal cancer: a call for a change
of approach in abdominoperineal resection. J Clin Oncol
2005;23:9257-64. CrossRef
18. Salerno G, Daniels IR, Brown
G. Magnetic resonance
imaging of the low rectum: defining the radiological
anatomy. Colorectal Dis 2006;8 Suppl 3:10-3. CrossRef
19. Allen SD, Gada V, Blunt DM.
Variation of mesorectal
volume with abdominal fat volume in patients with rectal
carcinoma: assessment with MRI. Br J Radiol 2007;80:242-7. CrossRef